OS Virtualization:-
- With the help of OS virtualization nothing is pre-installed or permanently loaded on the local device and no-hard disk is needed. Everything runs from the network using a kind of virtual disk.
- This virtual disk is actually a disk image file stored on a remote server, SAN (Storage Area Network) or NAS (Non-volatile Attached Storage).
- The client will be connected by the network to this virtual disk and will boot with the Operating System installed on the virtual disk.
How does OS Virtualization works?
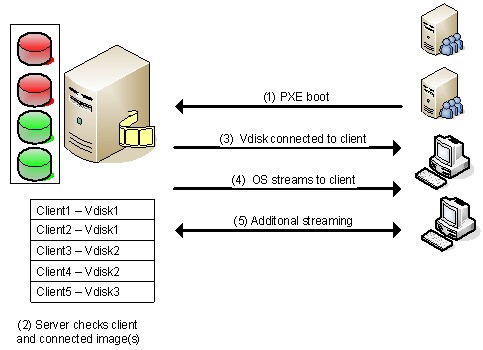
- Connecting to the OS Virtualization server:- First we start the machine and set up the connection with the OS Virtualization server. Most of the products offer several possible methods to connect with the server. One of the most popular and used methods is using a PXE service, but also a boot strap is used a lot (because of the disadvantages of the PXE service). Although each method initializes the network interface card (NIC), receiving a (DHCP-based) IP address and a connection to the server.
- Connecting the Virtual Disk:-When the connection is established between the client and the server, the server will look into its database for checking the client is known or unknown and which virtual disk is assigned to the client. When more than one virtual disk are connected then a boot menu will be displayed on the client side. If only one disk is assigned, that disk will be connected to the client which is mentioned in step number 3.
- VDisk connected to the client:-After the desired virtual disk is selected by the client, that virtual disk is connected through the OS Virtualization server . At the back-end, the OS Virtualization server makes sure that the client will be unique (for example computer name and identifier) within the infrastructure.
- OS is "streamed" to the client:-As soon the disk is connected the server starts streaming the content of the virtual disk. The software knows which parts are necessary for starting the operating system smoothly, so that these parts are streamed first. The information streamed in the system should be stored somewhere (i.e. cached). Most products offer several ways to cache that information. For examples on the client hard disk or on the disk of the OS Virtualization server.
- Additional Streaming:-After that the first part is streamed then the operating system will start to run as expected. Additional virtual disk data will be streamed when required for running or starting a function called by the user (for example starting an application available within the virtual disk).