Private Cloud:-
Private Cloud:The Private cloud allows the accessibility of systems and services within the organization. Private cloud is operated only within a particular organization. But it will be managed internally or by third party.
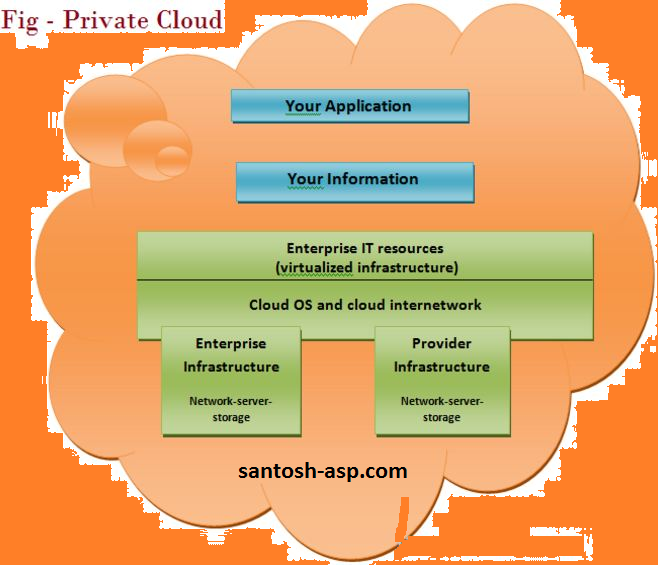
Private cloud infrastructure is a dedicated infrastructure provided to one single organization or client.
Private clouds or enterprise clouds are used by organizations that have security, compliance and data privacy as their top priority.
Private clouds are deployed inside firewalls and offer robust IT security for the organization. If a data center infrastructure is already available with the organization the private cloud can be implemented in-house.
However, for having in-house private clouds the organization needs to invest heavily in running and maintaining the infrastructure which can result in significant capital expenditure. This can be a major setback for organizations thinking to reduce IT budgets.
Private cloud services are also made available by cloud service providers or data centers. Examples of private cloud implementations can be easily found in areas such as banking and financial institutions, large enterprise organizations, government organizations, etc. where only authorized users are able to access the system.
Advantage of Private Cloud Model:
Disadvantages of Private Cloud Model:
Private cloud infrastructure is a dedicated infrastructure provided to one single organization or client.
Private clouds or enterprise clouds are used by organizations that have security, compliance and data privacy as their top priority.
Private clouds are deployed inside firewalls and offer robust IT security for the organization. If a data center infrastructure is already available with the organization the private cloud can be implemented in-house.
However, for having in-house private clouds the organization needs to invest heavily in running and maintaining the infrastructure which can result in significant capital expenditure. This can be a major setback for organizations thinking to reduce IT budgets.
Private cloud services are also made available by cloud service providers or data centers. Examples of private cloud implementations can be easily found in areas such as banking and financial institutions, large enterprise organizations, government organizations, etc. where only authorized users are able to access the system.

Advantage of Private Cloud Model:
- High security and privacy: Private cloud resources are shared from distinct pool of resources and hence highly secured.
- More Control: Private clouds have more control on its resources and hardware than public cloud because it is accessed only within the boundary of an organization.
- Superior Performance: Normally private clouds are deployed inside the firewall of the organization’s intranet which ensures efficiency and good network performance.
- Easy Customization: The hardware and other resources can be customized easily by the company.
- Compliance: Compliance is achieved easily in private clouds.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud Model:
- More Cost: Private Cloud is having more cost than public clouds.
- Restriction:Private cloud is only accessible locally and it is very difficult to deploy globally.
- Inflexible Price: In order to fulfill demands, purchasing new hardware is very costly.
- Less Scalability: Private clouds are scaled only within capacity of internal hosted resources.
- Vendor lock-in: This can be a major impediment in private cloud adoption especially when the hardware and infrastructure is outsourced. This is a service delivery technique where the client company is forced to continue with the same service provider, thus preventing the client to migrate to another vendor.
- Capacity ceiling: Due to physical hardware limitations with the service provider, there could be a capacity ceiling to handle only certain amount of servers or storage.
- Under-utilization: In some instances the resources subscribed can be under-utilized. Hence, optimizing the utilization of all resources is a challenge.