Oracle Function:-
A function is a subprogram that is used to return a single value. You must declare and define a function before invoking it. It can be declared and defined at a same time or can be declared first and defined later in the same block.
How to create function in Oracle
Syntax:-
You must have define some parametrs before creating a procedure or a function. These parameters are
IN: It is a default parameter. It passes the value to the subprogram.
OUT: It must be specified. It returns a value to the caller.
IN OUT: It must be specified. It passes an initial value to the subprogram and returns an updated value to the caller.
Example (1):- Let's see a simple example to create a function.
Now write another program to call the function.
Out Put:-

Example (2):- Let's take an example to demonstrate Declaring, Defining and Invoking a simple PL/SQL function which will compute and return the maximum of two values.
Out Put:-

Example (3):- Oracle function example using table Let's take a Employee table. This example illustrates creating and calling a standalone function. This function will return the total number of Employees in the Employee table.
We create table named with Employee and insert some records as shown in below:
Now, We create function
After the execution of above code, you will get the following result.
Calling totalEmployees Function:-
After the execution of above code in SQL prompt, you will get the following result.
Oracle Recursive Function:-
You already know that a program or a subprogram can call another subprogram. When a subprogram calls itself, it is called recursive call and the process is known as recursion.
Example (4):- Example to calculate the factorial of a number
Let's take an example to calculate the factorial of a number. This example calculates the factorial of a given number by calling itself recursively.
After the execution of above code at SQL prompt, it produces the following result.
Drop Function in Oracle:- If you want to remove your created function from the database, you should use the following syntax.
Syntax:-
How to create function in Oracle
Syntax:-
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name [ (parameter [,parameter]) ] RETURN return_datatype IS | AS [declaration_section] BEGIN executable_section [EXCEPTION exception_section] END [function_name];
You must have define some parametrs before creating a procedure or a function. These parameters are
IN: It is a default parameter. It passes the value to the subprogram.
OUT: It must be specified. It returns a value to the caller.
IN OUT: It must be specified. It passes an initial value to the subprogram and returns an updated value to the caller.
Example (1):- Let's see a simple example to create a function.
create or replace function addition(firstno in number, secondno in number) return number is result number(8); begin result :=firstno+secondno; return result; end; /
Now write another program to call the function.
DECLARE result number(2); BEGIN result := addition(22,11); dbms_output.put_line('Addition is: ' || result); END; /
Out Put:-

Example (2):- Let's take an example to demonstrate Declaring, Defining and Invoking a simple PL/SQL function which will compute and return the maximum of two values.
DECLARE p number; q number; r number; FUNCTION findMax(x IN number, y IN number) RETURN number IS z number; BEGIN IF x > y THEN z:= x; ELSE Z:= y; END IF; RETURN z; END; BEGIN p:= 23; q:= 45; r := findMax(p, q); dbms_output.put_line(' Maximum of (23,45): ' || r); END; /
Out Put:-

Example (3):- Oracle function example using table Let's take a Employee table. This example illustrates creating and calling a standalone function. This function will return the total number of Employees in the Employee table.
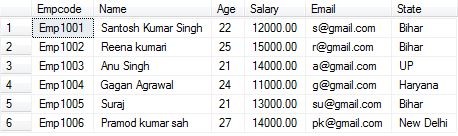
We create table named with Employee and insert some records as shown in below:
CREATE TABLE Employee ( Empcode varchar2(30) primary key, Name varchar2(100), Age number(5), Salary numeric(10,2), Email varchar2(200), State varchar2(100) CONSTRAINT Employee_pk PRIMARY KEY (Empcode) ); //Insert some records as shown below:- Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1001','Santosh Kumar Singh',22,12000,'s@gmail.com','Bihar') Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1002','Reena kumari',25,15000,'r@gmail.com','Bihar') Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1003','Anu Singh',21,14000,'a@gmail.com','UP') Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1004','Gagan Agrawal',24,11000,'g@gmail.com','Haryana') Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1005','Suraj',21,13000,'su@gmail.com','Bihar') Insert into Employee(Empcode,Name,Age,Salary,Email,State) values('Emp1006','Pramod kumar sah',27,14000,'pk@gmail.com','New Delhi')

Now, We create function
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION totalEmployees RETURN number IS total number(2) := 0; BEGIN SELECT count(*) into total FROM Employee; RETURN total; END; /
After the execution of above code, you will get the following result.
Function created.
Calling totalEmployees Function:-
DECLARE c number(2); BEGIN c := totalEmployees(); dbms_output.put_line('Total no. of Employee: ' || c); END; /
After the execution of above code in SQL prompt, you will get the following result.
Total no. of Employees: 6 PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Oracle Recursive Function:-
You already know that a program or a subprogram can call another subprogram. When a subprogram calls itself, it is called recursive call and the process is known as recursion.
Example (4):- Example to calculate the factorial of a number
Let's take an example to calculate the factorial of a number. This example calculates the factorial of a given number by calling itself recursively.
DECLARE num number; factorial number; FUNCTION fact(x number) RETURN number IS f number; BEGIN IF x=0 THEN f := 1; ELSE f := x * fact(x-1); END IF; RETURN f; END; BEGIN num:= 6; factorial := fact(num); dbms_output.put_line(' Factorial '|| num || ' is ' || factorial); END; /
After the execution of above code at SQL prompt, it produces the following result.
Factorial 6 is 720 PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Drop Function in Oracle:- If you want to remove your created function from the database, you should use the following syntax.
Syntax:-
DROP FUNCTION function_name;