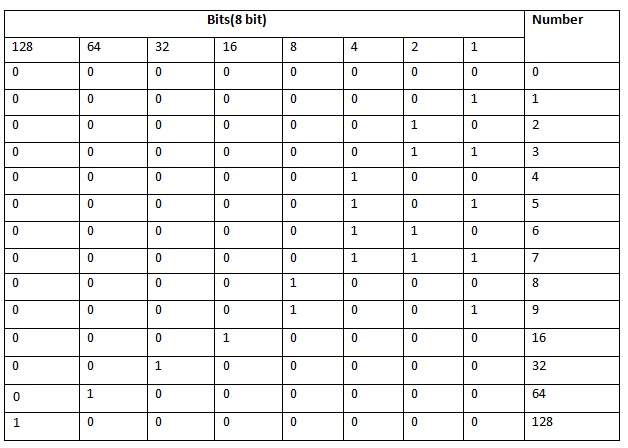
- The BitArray class manages a compact array of bit values, which are represented as Booleans, where true indicates that the bit is on (1) and false indicates the bit is off (0).
- It is used when you need to store the bits but do not know the number of bits in advance.
- You can access items from the BitArray collection by using an integer index, which starts from zero.
Methods and Properties of the BitArray Class:-
Methods of the BitArray Class:-
| Sr.No. | Methods |
|---|---|
| 1 | public BitArray And(BitArray value); Performs the bitwise AND operation on the elements in the current BitArray against the corresponding elements in the specified BitArray. |
| 2 | public bool Get(int index); Gets the value of the bit at a specific position in the BitArray. |
| 3 | public BitArray Not(); Inverts all the bit values in the current BitArray, so that elements set to true are changed to false, and elements set to false are changed to true. |
| 4 | public BitArray Or(BitArray value); Performs the bitwise OR operation on the elements in the current BitArray against the corresponding elements in the specified BitArray. |
| 5 | public void Set(int index, bool value); Sets the bit at a specific position in the BitArray to the specified value. |
| 6 | public void SetAll(bool value); Sets all bits in the BitArray to the specified value. |
| 7 | public BitArray Xor(BitArray value); Performs the bitwise eXclusive OR operation on the elements in the current BitArray against the corresponding elements in the specified BitArray. |
Properties of the BitArray Class:-
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Count | Gets the number of elements contained in the BitArray. |
| IsReadOnly | Gets a value indicating whether the BitArray is read-only. |
| Item | Gets or sets the value of the bit at a specific position in the BitArray. |
| Length | Gets or sets the number of elements in the BitArray. |
using System; using System.Collections; class BitArrayDemo { public BitArrayDemo() { Console.WriteLine("This is BitArray Demo::\n"); } public void Show() { //creating two bit arrays of size 8 BitArray ba1 = new BitArray(8); BitArray ba2 = new BitArray(8); byte[] a = { 60 }; byte[] b = { 13 }; //storing the values 60, and 13 into the bit arrays ba1 = new BitArray(a); ba2 = new BitArray(b); //content of ba1 Console.WriteLine("Bit array ba1: 60"); for (int i = 0; i < ba1.Count; i++) { Console.Write("{0, -6} ", ba1[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); //content of ba2 Console.WriteLine("Bit array ba2: 13"); for (int i = 0; i < ba2.Count; i++) { Console.Write("{0, -6} ", ba2[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); BitArray ba3 = new BitArray(8); ba3 = ba1.And(ba2); //content of ba3 Console.WriteLine("Bit array ba3 after AND operation: 12"); for (int i = 0; i < ba3.Count; i++) { Console.Write("{0, -6} ", ba3[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); ba3 = ba1.Or(ba2); //content of ba3 Console.WriteLine("Bit array ba3 after OR operation: 61"); for (int i = 0; i < ba3.Count; i++) { Console.Write("{0, -6} ", ba3[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); } } class Test { static void Main(string[] args) { BitArrayDemo objBAL = new BitArrayDemo(); objBAL.Show(); Console.ReadLine(); } }