Simple explanation of this keyword to make user understand its way of using and implementation.
The this keyword refers to the current instance of the class. It can be used to access members from within constructors, instance methods, and instance accessors.
Static constructors and member methods do not have a this pointer because they are not instantiated.
When you are writing code in method or property of a class, using "this" will allow you to make use of the intellisense.
this keyword is used when you want to track the instance, which is invoked to perform some calculation or further processing relating to that instance.
Let me explain you with a simple practical demonstration.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace this_example
{
class Program
{
public class
Demo
{
string name;
int age;
public Demo(int
age, string name)
{
age = age;
name = name;
}
public void
Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("Your age is :"
+ age.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Your name is : "
+ name);
}
}
static void
Main(string[] args)
{
int _age;
string _name;
Console.WriteLine("Enter your age : ");
_age = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter your name : ");
_name = Console.ReadLine();
Demo obj = new
Demo(_age, _name);
obj.Show();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
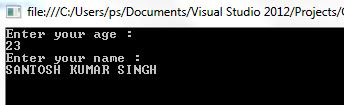
Output of the above program will be:
See your not getting any value. Because in the program the local data members age, name have precedence over instance members.
Note the program will give a warning not error (Assignment made to some variable; did you mean to assign something else?)
We have to use this keyword to refer to the instance members.
Now I do a slight change in the program using this keyword.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace this_example
{
class Program
{
public class
Demo
{
int age;
string name;
public Demo(int
age, string name)
{
// Have made change here included this keyword
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
{
Console.WriteLine("Your age is :"
+ age.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Your name is : "
+ name);
}
}
static void
Main(string[] args)
{
int _age;
string _name;
Console.WriteLine("Enter your age : ");
_age = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter your name : ");
_name = Console.ReadLine();
Demo obj = new Demo(_age, _name)
obj.Show();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
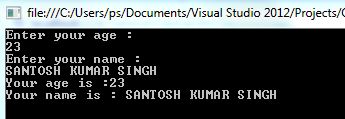
See the output.
I think now this keyword would be clear to you.
The program is not complete implementation of this keyword but it tries to make you explain how it works and when to use.