ng-include directive in AngularJS:-
ng-include directive is used to embed an HTML page into another HTML page. This technique is extremely useful when you want to reuse a specific view in multiple pages in your application.
The value of ng-include directive can be the name of the HTML page that you want to reuse or a property on the $scope object that points to the reusable HTML page.
EmployeeList.html : This is the HTML page that we intend to reuse on multiple HTML pages
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th>Salary</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr ng-repeat="employee in employees">
<td> {{ employee.name }} </td>
<td> {{ employee.gender}} </td>
<td> {{ employee.salary}} </td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
Script.js :
var app = angular
.module("myModule", [])
.controller("myController", function ($scope) {
var employees = [
{ name: "Ben", gender: "Male", salary: 55000 },
{ name: "Sara", gender: "Female", salary: 68000 },
{ name: "Mark", gender: "Male", salary: 57000 },
{ name: "Pam", gender: "Female", salary: 53000 },
{ name: "Todd", gender: "Male", salary: 60000 }
];
$scope.employees = employees;
});
HTMLPage1.html : This is the HTML page where we want to reuse EmployeeList.html. Notice that we are using ng-include directive and the value for it is the name of the HTML file that we want to reuse.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<script src="Scripts/angular.js"></script>
<script src="Scripts/Script.js"></script>
<link href="Styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body ng-app="myModule">
<div ng-controller="myController">
<div ng-include="'EmployeeList.html'">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
In this example, we have specified the name of the HTML file in the view. You can also have a property attached to the $scope object that points to the HTML file that you want to reuse , and use that property with ng-include directive. Here are the changes required to use a model property with ng-include directive.
Script.js : Notice, in the controller function we have employeeList property attached to the $scope object. This property points to the EmployeeList.html file that we want to reuse.
var app = angular
.module("myModule", [])
.controller("myController", function ($scope) {
var employees = [
{ name: "Ben", gender: "Male", salary: 55000 },
{ name: "Sara", gender: "Female", salary: 68000 },
{ name: "Mark", gender: "Male", salary: 57000 },
{ name: "Pam", gender: "Female", salary: 53000 },
{ name: "Todd", gender: "Male", salary: 60000 }
];
$scope.employees = employees;
$scope.employeeList = "EmployeeList.html";
});
HTMLPage1.html : Set the property employeeList that you have attached to the $scope object, as the value for ng-include directive
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<script src="Scripts/angular.js"></script>
<script src="Scripts/Script.js"></script>
<link href="Styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body ng-app="myModule">
<div ng-controller="myController">
<div ng-include="employeeList"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Example (1):- Create an HTML page with a dropdownlist that allows the user to select the view - Table or List. Depending on the selection we want to load the respective HTML page into the current HTML page i.e HTMLPage1.html If the user selects Table from the dropdownlist, the employee data should be presented using a Table
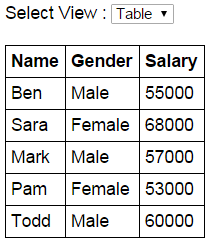
If the user selects List from the dropdownlist, the employee data should be presented using an unordered list

EmployeeTable.html : This HTML page presents the employee data using a table element
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th>Salary</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr ng-repeat="employee in employees">
<td> {{ employee.name }} </td>
<td> {{ employee.gender}} </td>
<td> {{ employee.salary}} </td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
EmployeeList.html : This HTML page presents the employee data using 2 unordered list elements
<ul ng-repeat="employee in employees">
<li>
{{employee.name}}
<ul>
<li>{{employee.gender}}</li>
<li>{{employee.salary}}</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
Script.js : The controller function attaches employeeView property to the $scope object and sets it to EmployeeTable.html. This means when the page is initially loaded the employee data will be presented using a table.
var app = angular
.module("myModule", [])
.controller("myController", function ($scope) {
var employees = [
{ name: "Ben", gender: "Male", salary: 55000 },
{ name: "Sara", gender: "Female", salary: 68000 },
{ name: "Mark", gender: "Male", salary: 57000 },
{ name: "Pam", gender: "Female", salary: 53000 },
{ name: "Todd", gender: "Male", salary: 60000 }
];
$scope.employees = employees;
$scope.employeeView = "EmployeeTable.html";
});
HTMLPage1.html : This HTML page loads either the EmployeeTable.html or EmployeeList.html page depending on the item the user has selected from the dropdownlist.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title></title>
<script src="Scripts/angular.js"></script>
<script src="Scripts/Script.js"></script>
<link href="Styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body ng-app="myModule">
<div ng-controller="myController">
Select View :
<select ng-model="employeeView">
<option value="EmployeeTable.html">Table</option>
<option value="EmployeeList.html">List</option>
</select>
<br /><br />
<div ng-include="employeeView">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
EmployeeList.html : This is the HTML page that we intend to reuse on multiple HTML pages
HTMLPage1.html : This is the HTML page where we want to reuse EmployeeList.html. Notice that we are using ng-include directive and the value for it is the name of the HTML file that we want to reuse.
In this example, we have specified the name of the HTML file in the view. You can also have a property attached to the $scope object that points to the HTML file that you want to reuse , and use that property with ng-include directive. Here are the changes required to use a model property with ng-include directive.
Example (1):- Create an HTML page with a dropdownlist that allows the user to select the view - Table or List. Depending on the selection we want to load the respective HTML page into the current HTML page i.e HTMLPage1.html If the user selects Table from the dropdownlist, the employee data should be presented using a Table

If the user selects List from the dropdownlist, the employee data should be presented using an unordered list

EmployeeTable.html : This HTML page presents the employee data using a table element
EmployeeList.html : This HTML page presents the employee data using 2 unordered list elements
Script.js : The controller function attaches employeeView property to the $scope object and sets it to EmployeeTable.html. This means when the page is initially loaded the employee data will be presented using a table.
HTMLPage1.html : This HTML page loads either the EmployeeTable.html or EmployeeList.html page depending on the item the user has selected from the dropdownlist.