You then have two options, the first one is to design the head, body and footer sections on each page. In this approach, you need to write more code on each page so ASP.NET 2.0 introduced "Master Pages" that helps enable this when using .aspx based pages or templates.
It is your second option. Razor also supports this concept with a feature called "layouts" that allow you to define a common site template, and then inherit its look and feel across all the views/pages on your web application.
Basic structure of Layout Page:-
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title> @Styles.Render("~/Content/css") @Scripts.Render("~/bundles/modernizr") </head> <body> @RenderBody() @Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery") @RenderSection("scripts", required: false) </body> </html>
Create an MVC Application:-
I will create an MVC application using Visual Studio 2012. So let's see step-by-step how to create a MVC application.
Step 1: Go to "File" -> "New" -> "Project...".
Step 2: Choose "ASP.NET MVC 4 Web Application" from the list, then give the application name "LayoutMvcApplication" and set the path in the location input where you want to create the application.
Step 3: Now choose the Project Template "Empty" and select "Razor" as the view engine from the dropdown list.
Create Layout for Application:-
A layout is used to provide a consistent look and feel of all pages of a web application so we create a layout for the web application. Let's see the procedure for that.
Step 1: Create a "Content" folder in the root directory of the web application.
Step 2: Create a Style Sheet "Site.css" under the content folder. That CSS file contains all CSS classes necessary for a consistent web application page design.
Step 3: Create a "Shared" folder under the "View" folder.
Step 4: Create a "_Layout.cshtml" file under the "Shared" folder. The file "_Layout.cshtml" represents the layout of each page in the application. Right-click on the Shared folder in Solution Explorer, then go to "Add" item and click on "View".
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title - Code Express</title> <link href="~/favicon.ico" rel="shortcut icon" type="image/x-icon" /> <link rel="stylesheet" href="@Url.Content("~/Content/Site.css")" /></head><body> <header> <div class="content-wrapper"> <div class="float-left"> <p class="site-title"> @Html.ActionLink("Code Express", "Index", "Home") </p> </div> <div class="float-right"> <nav> <ul id="menu"> <li>@Html.ActionLink("Home", "Index", "Home")</li> <li>@Html.ActionLink("About", "About", "Home")</li> </ul> </nav> </div> </div> </header> <div id="body"> @RenderSection("featured", required: false) <section class="content-wrapper main-content clear-fix"> @RenderBody() </section> </div> <footer> <div class="content-wrapper"> <div class="float-left"> <p>© @DateTime.Now.Year – Code Express</p> </div> </div> </footer> </body> </html>
In this layout, we are using an HTML helper method and some other system defined methods so let's see these methods one by one.
Url.Content():Content()method is a method ofUrlHelperclass. It converts a virtual (relative) path to an application absolute path. It has one parameter ofstringtype that is a virtual path of the content. It returns an application's absolute path. If the specified content path (parameter of the method) does not start with the tilde (~) character, then this method returnscontentPathunchanged.Url.Content()ensures that all links work no matter if the site is in a virtual directory or in the web site root.Html.ActionLink(): The easiest way to render an HTML link in is to use theHTML.ActionLink()helper. With MVC, theHtml.ActionLink()does not link to a view. It creates a link to a controller action.ActionLink()is an extension method of theHtmlHelperclass. It returns an anchor element (an element) that contains the virtual path of the specified action. When you use anActionLink()method, then you need to pass threestringparameters. The parameters arelinkText(the inner text of the anchor element),actionName(the name of the action) andcontrollerName(the name of the controller).RenderSection():RenderSection()is a method of theWebPageBaseclass. Scott wrote at one point, the first parameter to the "RenderSection()" helper method specifies the name of the section we want to render at that location in the layout template. The second parameter is optional, and allows us to define whether the section we are rendering is required or not. If a section is "required", then Razor will throw an error at runtime if that section is not implemented within a view template that is based on the layout file (that can make it easier to track down content errors). It returns the HTML content to render.RenderBody(): In layout pages, renders the portion of a content page that is not within a named section. It returns the HTML content to render.RenderBodyis required, since it's what renders each view.
The _ViewStart File:- The "_ViewStart" file in the Views folder contains the following content:
@{ Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml"; }
You need to create a controller that contains an action method to render the view on the user interface. I will create a HomeController controller with two action methods, one is Index and the other is About.
Both action methods execute when the request type is GET and renders a view on the browser. So use the following procedure:
Step 1: Right-click on the Controllers folder under Solution Explorer, then go to "Add" and click on "Controller".
Step 2: Give the name HomeController for the Controller name input and select "Empty MVC controller" from the Template dropdown list. After that, click on "Add".
Now you need to write the following code in the "HomeController.cs" file:
using System.Web.Mvc; namespace LayoutMvcApplication.Controllers { public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Index() { return View(); } public ActionResult Index() { return View(); } } }
Create View in MVC Application:-
You need to create two views (Index and About) that inherit the "_Layout" view via the "_ViewStart"
view so you need to use the following procedure.
Step 1: Right-click on the Index() action method under the "HomeController.cs" file, then click on "Add View".
Step 2: Leave Add New screen unchanged and click on "Add".
Now you should write the following code in your web application index view:
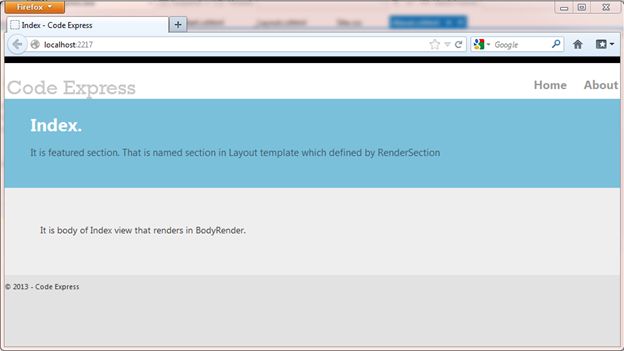
@{ ViewBag.Title = "Index"; } @section featured { <section class="featured"> <div class="content-wrapper"> <hgroup class="title"> <h1>@ViewBag.Title.</h1> </hgroup> <p> It is featured section. That is named section in Layout template that defined by RenderSection </p> </div> </section> } <p> It is body of Index view that renders in BodyRender.</p>
You can follow the same steps for the About view and create it.
Now run the application and get out put.