Clustered and Non-Clustered indexes in SQL Server
Clustered Index:-
Now, we are going to create table and named tblEmployee as shown in below.
In the above table tblEmployee EmpId is as primary key. Primary key, constraint create clustered indexes automatically if no clustered index already exists on the table and a nonclustered index is not specified when you create the PRIMARY KEY constraint.
To confirm this, execute the following code, which will show a unique clustered index created on the Id column.
After excute the above query we will the follwing output.

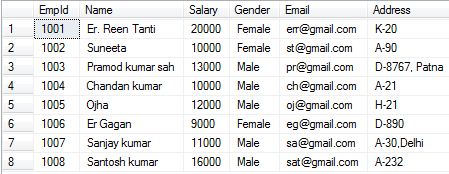
Now, we insert some records in tblEmployee as shown in below. We insert values for EmpId column are not in a sequential order.
Execute the following SELECT following query in SQL Server.
Now, let we create clustered index on 2 columns. To do this we first have to drop the existing clustered index on the EmpId column. For do this we excute the following code and get error.
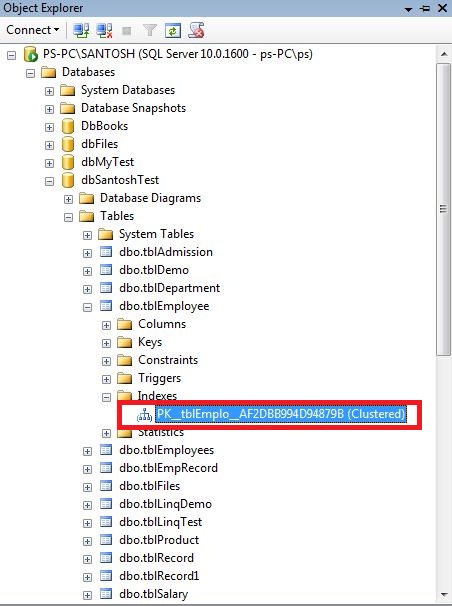
We will study about the role of unique index in the next chapter. To successfully delete the clustered index. For this Go to--->> Object explorer window --->>Select Database in which we are working--->>Expand the table which one we are working--->>Expand the Indexes --->>Right click on PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B index and select DELETE.
We are using database dbSantoshTest and table tblEmployee as shwon in below.
Now, create a composite clustered Index on the Name and Salary columns on tblEmployee table shown as below.
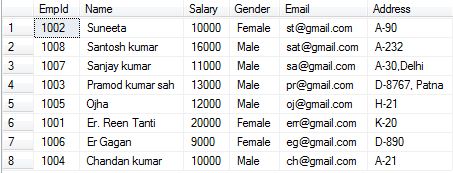
Now, we run the select query then output will shown as---->>we should see the data physically arranged, FIRST by Name in descending order and then by Salary in ascending order.
Non Clustered Index:
Example:-
What is difference between Clustered and NonClustered Index:
- Clustered indexes sort and store the data rows in the table or view based on their key values. These are the columns included in the index definition. There can be only one clustered index per table, because the data rows themselves can be sorted in only one order.
- The only time the data rows in a table are stored in sorted order is when the table contains a clustered index. When a table has a clustered index, the table is called a clustered table. If a table has no clustered index, its data rows are stored in an unordered structure called a heap.
- A clustered index determines the physical order of data in a table. For this reason, a table can have only one clustered index.
Now, we are going to create table and named tblEmployee as shown in below.
CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpId int Primary Key, Name nvarchar(100), Salary int, Gender nvarchar(30), Email nvarchar(200), Address nvarchar(50) )
In the above table tblEmployee EmpId is as primary key. Primary key, constraint create clustered indexes automatically if no clustered index already exists on the table and a nonclustered index is not specified when you create the PRIMARY KEY constraint.
To confirm this, execute the following code, which will show a unique clustered index created on the Id column.
execute sp_helpindex tblEmployee
After excute the above query we will the follwing output.

Now, we insert some records in tblEmployee as shown in below. We insert values for EmpId column are not in a sequential order.
INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1004,'Chandan kumar',10000,'Male','ch@gmail.com','A-21') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1003,'Pramod kumar sah',13000,'Male','pr@gmail.com','D-8767, Patna') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1001,'Er. Reen Tanti',20000,'Female','err@gmail.com','K-20') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1006,'Er Gagan',9000,'Female','eg@gmail.com','D-890') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1002,'Suneeta',10000,'Female','st@gmail.com','A-90') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1005,'Ojha',12000,'Male','oj@gmail.com','H-21') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1007,'Sanjay kumar',11000,'Male','sa@gmail.com','A-30,Delhi') INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES(1008,'Santosh kumar',16000,'Male','sat@gmail.com','A-232')
Execute the following SELECT following query in SQL Server.
Select * from tblEmployee

- When we execute the above select query we can see that all the rows in the table are arranged in an ascending order based on the EmpId column. This is because a clustered index determines the physical order of data in a table, and we have got a clustered index on the EmpId column.
- Because of the fact that, a clustered index dictates the physical storage order of the data in a table, a table can contain only one clustered index. If you take the example of tblEmployee table, the data is already arranged by the Id column, and if we try to create another clustered index on the Name column, the data needs to be rearranged based on the NAME column, which will affect the ordering of rows that's already done based on the EmpId column.
- For this reason, SQL server doesn't allow us to create more than one clustered index per table. Example- if we try to create more than one clustered index in table then following error will be occured.
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX IX_tblEmployee_Salary ON tblEmployee(Salary)
Error:-
Msg 1902, Level 16, State 3, Line 1
Cannot create more than one clustered index on table 'tblEmployee'. Drop the existing clustered index 'tblEmployee.PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B' before creating another. - A clustered index is analogous to a telephone directory, where the data is arranged by the last name.
Now, let we create clustered index on 2 columns. To do this we first have to drop the existing clustered index on the EmpId column. For do this we excute the following code and get error.
Drop index tblEmployee.PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B
Msg 3723, Level 16, State 4, Line 1
An explicit DROP INDEX is not allowed on index 'tblEmployee.PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B'. It is being used for PRIMARY KEY constraint enforcement.
An explicit DROP INDEX is not allowed on index 'tblEmployee.PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B'. It is being used for PRIMARY KEY constraint enforcement.
We will study about the role of unique index in the next chapter. To successfully delete the clustered index. For this Go to--->> Object explorer window --->>Select Database in which we are working--->>Expand the table which one we are working--->>Expand the Indexes --->>Right click on PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBB994D94879B index and select DELETE.
We are using database dbSantoshTest and table tblEmployee as shwon in below.

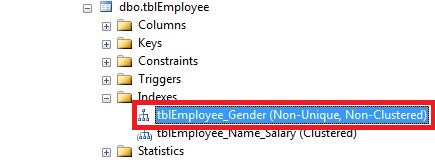
Now, create a composite clustered Index on the Name and Salary columns on tblEmployee table shown as below.
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX tblEmployee_Name_Salary ON tblEmployee(Name DESC, Salary ASC)
Now, we run the select query then output will shown as---->>we should see the data physically arranged, FIRST by Name in descending order and then by Salary in ascending order.

Non Clustered Index:
- A nonclustered index is analogous to an index in a textbook. The data is stored in one place, the index in another place.
- The index will have pointers to the storage location of the data. Since, the nonclustered index is stored separately from the actual data, a table can have more than one non clustered index, just like how a book can have an index by Chapters at the beginning and another index by common terms at the end.
- In the index itself, the data is stored in an ascending or descending order of the index key, which doesn't in any way influence the storage of data in the table.
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX Index_Name ON table_name(column_name)
Example:-
CREATE CLUSTERED INDEX tblEmployee_Name_Salary ON tblEmployee(Name DESC, Salary ASC)

What is difference between Clustered and NonClustered Index:
| S.No. | Clustered Index | NonClustered Index |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Only one clustered index per table. | More than one non clustered index in a table. |
| 2. | Clustered index is faster than a non clustered index, because, the non-clustered index has to refer back to the table, if the selected column is not present in the index. | Non clustered index is slower than clustered index. |
| 3. | Clustered index determines the storage order of rows in the table, and hence doesn't require additional disk space. | Non Clustered index is stored seperately from the table, additional storage space is required. |