NULL Values In SQL
- NULL values represent missing unknown data.
- By default, a table column can hold NULL values.
- If a column in a table is optional, we can insert a new record or update an existing record without adding a value to this column. This means that the field will be saved with a NULL value.
- NULL values are treated differently from other values.
- NULL is used as a placeholder for unknown or inapplicable values.
- It is not possible to compare NULL and 0; they are not equivalent.
First of all we create a table in SQL Server and insert some as shown in below.
CREATE TABLE tblTestSample ( Id int primary key,FirstName varchar(50),LastName varchar(50) Null,Email nvarchar(100) ) ----------INSERT SOME RECORDS---------- INSERT INTO tblTestSample VALUES(1001,'Santosh','','s@gmail.com') INSERT INTO tblTestSample VALUES(1002,'POOJA KUMARI','','p@gmail.com') INSERT INTO tblTestSample VALUES(1003,'POOJA KUMARI','sharma','pr@gmail.com') INSERT INTO tblTestSample VALUES(1004,'Kalpna','','k@gmail.com') INSERT INTO tblTestSample VALUES(1005,'Pramod','Sah','p@gmail.com')
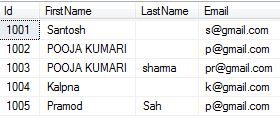
SELECT * FROM tblTestSample WHERE LastName IS NULL ---------------- IS NOT NULL----------------- SELECT * FROM tblTestSample WHERE LastName IS NOT NULL