CREATE INDEX in SQL
First of all we are going to study why Index is needed.
Why Indexes?
Suppose that you have a book. This book has no index page. Now, we have to search a particular chapter or topic. What will be do?. We go to turn each and every page until we did not find chapter or topic. It takes more time. Now, if this book has index page. Again we have to search chapter or topic. What will be do?. We go to index page and see page number and directly go to chapter or topic. It takes short time. So, that's all Indexes is needed.
Same concept is applied on table in SQL.
What is Index?
Note:-
Updating a table with indexes takes more time than updating a table without (because the indexes also need an update). So you should only create indexes on columns (and tables) that will be frequently searched against.
Syntax:-
Example:-
How to create Index graphically in SQL Server:-
We have to follow following some steps for creating Index in SQL Server.
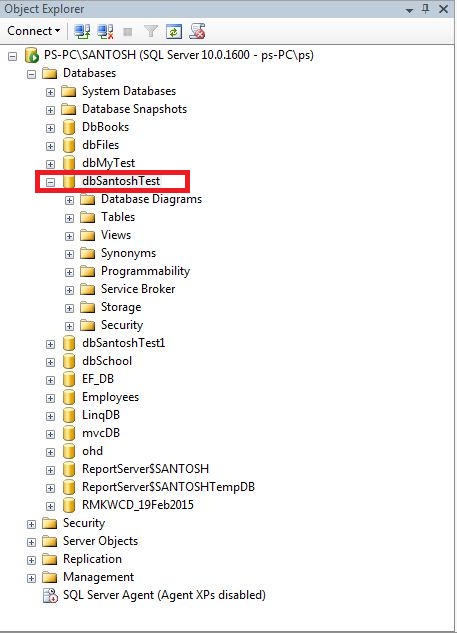
Step1:- In the Object Explorer, expand the Databases folder and then specific database you are working with. We are working in dbSantosTest As shown in below.
Step2:-Expand the Tables folder
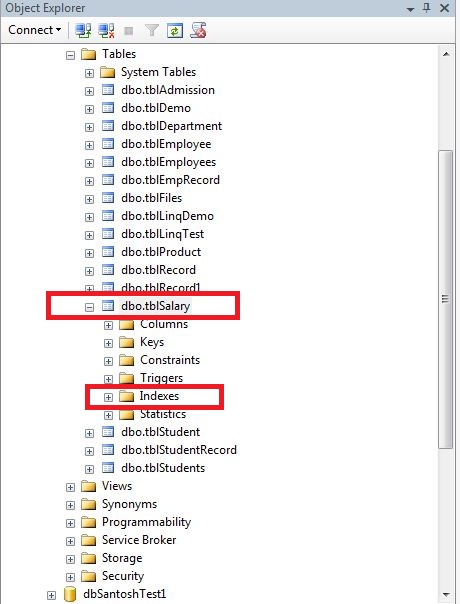
Step3:-Expand the Table on which you want to create the index
Step4:-Right click on the Indexes folder and select New Index
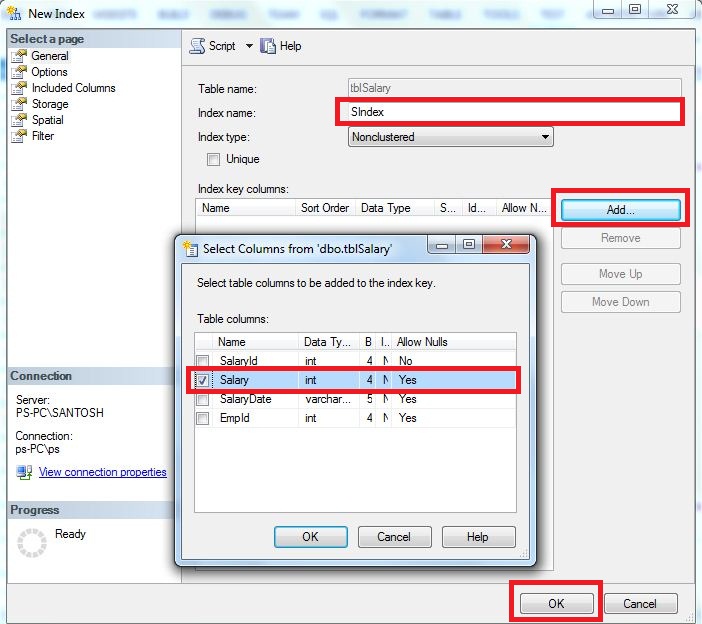
Step5:-In the New Index dialog box, type in a meaningful name
Step6:-Select the Index Type and specify Unique or Non Unique Index
Step7:- Click the Add
Step8:-Select the columns that you want to add as index key
Step9:-Click OK
Step10:-Save the table
Type of Index in SQL Server:- There are many types of Index in SQL Server.
Why Indexes?
Suppose that you have a book. This book has no index page. Now, we have to search a particular chapter or topic. What will be do?. We go to turn each and every page until we did not find chapter or topic. It takes more time. Now, if this book has index page. Again we have to search chapter or topic. What will be do?. We go to index page and see page number and directly go to chapter or topic. It takes short time. So, that's all Indexes is needed.
Same concept is applied on table in SQL.
What is Index?
- An index can be created in a table to find data more quickly and efficiently.
- The users cannot see the indexes, they are just used to speed up searches/queries.
- Indexes are created on tables and views.
- Index on a table or a view, is very similar to an index that we find in a book.
Note:-
Updating a table with indexes takes more time than updating a table without (because the indexes also need an update). So you should only create indexes on columns (and tables) that will be frequently searched against.
Syntax:-
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_name)
Example:-
---------For single column----------------- CREATE INDEX SIndex ON tblSalary(Salary) ---------For multiple columns------------- CREATE INDEX SIndex ON tblSalary(Salary,SalaryDate)
How to create Index graphically in SQL Server:-
We have to follow following some steps for creating Index in SQL Server.
Step1:- In the Object Explorer, expand the Databases folder and then specific database you are working with. We are working in dbSantosTest As shown in below.

Step2:-Expand the Tables folder
Step3:-Expand the Table on which you want to create the index

Step4:-Right click on the Indexes folder and select New Index
Step5:-In the New Index dialog box, type in a meaningful name
Step6:-Select the Index Type and specify Unique or Non Unique Index
Step7:- Click the Add
Step8:-Select the columns that you want to add as index key
Step9:-Click OK
Step10:-Save the table

Type of Index in SQL Server:- There are many types of Index in SQL Server.
- Clustered :- A clustered index sorts and stores the data rows of the table or view in order based on the clustered index key. The clustered index is implemented as a B-tree index structure that supports fast retrieval of the rows, based on their clustered index key values.
- Nonclustered:- A nonclustered index can be defined on a table or view with a clustered index or on a heap. Each index row in the nonclustered index contains the nonclustered key value and a row locator. This locator points to the data row in the clustered index or heap having the key value. The rows in the index are stored in the order of the index key values, but the data rows are not guaranteed to be in any particular order unless a clustered index is created on the table.
- Unique:- A unique index ensures that the index key contains no duplicate values and therefore every row in the table or view is in some way unique. Uniqueness can be a property of both clustered and nonclustered indexes.
- Index with included columns:- A nonclustered index that is extended to include nonkey columns in addition to the key columns.
- Index on computed columns:- An index on a column that is derived from the value of one or more other columns, or certain deterministic inputs.
- Filtered:- An optimized nonclustered index, especially suited to cover queries that select from a well-defined subset of data. It uses a filter predicate to index a portion of rows in the table. A well-designed filtered index can improve query performance, reduce index maintenance costs, and reduce index storage costs compared with full-table indexes.
- Spatial:- A spatial index provides the ability to perform certain operations more efficiently on spatial objects (spatial data) in a column of the geometry data type. The spatial index reduces the number of objects on which relatively costly spatial operations need to be applied.
- Columnstore:- An xVelocity memory optimized columnstore index based on vertical partitioning of the data by columns, stored as large objects (LOB).
- XML:- A shredded, and persisted, representation of the XML binary large objects (BLOBs) in the xml data type column.
- Full-text:- A special type of token-based functional index that is built and maintained by the Microsoft Full-Text Engine for SQL Server. It provides efficient support for sophisticated word searches in character string data.