Integrate Controller, View and Model:
We have already created StudentController, model and view in the previous sections, but we have not integrated all these components in-order to run it.
The following code snippet shows StudentController and Student model class & view created in the previous sections.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MVC_BasicTutorials.Controllers
{
public class StudentController : Controller
{
// GET: Student
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
namespace MVC_BasicTutorials.Models
{
public class Student
{
public int StudentId { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
}
@model IEnumerable<MVC_BasicTutorials.Models.Student>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.StudentName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Age)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.StudentName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Age)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.StudentId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.StudentId }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.StudentId })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
Now, to run it successfully, we need to pass a model object from controller to Index view. As you can see in the above Index.cshtml, it uses IEnumerable of Student as a model object. So we need to pass IEnumerable of Student model from the Index action method of StudentController class as shown below.
public class StudentController : Controller
{
// GET: Student
public ActionResult Index()
{
var studentList = new List<Student>{
new Student() { StudentId = 1, StudentName = "John", Age = 18 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 2, StudentName = "Steve", Age = 21 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 25 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 4, StudentName = "Ram" , Age = 20 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 5, StudentName = "Ron" , Age = 31 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 4, StudentName = "Chris" , Age = 17 } ,
new Student() { StudentId = 4, StudentName = "Rob" , Age = 19 }
};
// Get the students from the database in the real application
return View(studentList);
}
}
As you can see in the above code, we have created a List of student objects for an example purpose (in real life applicatoin, you can fetch it from the database). We then pass this list object as a parameter in the View() method. The View() method is defined in base Controller class, which automatically binds model object to the view.
Now, you can run the MVC project by pressing F5 and navigate to http://localhost/Student. You will see following view in the browser.
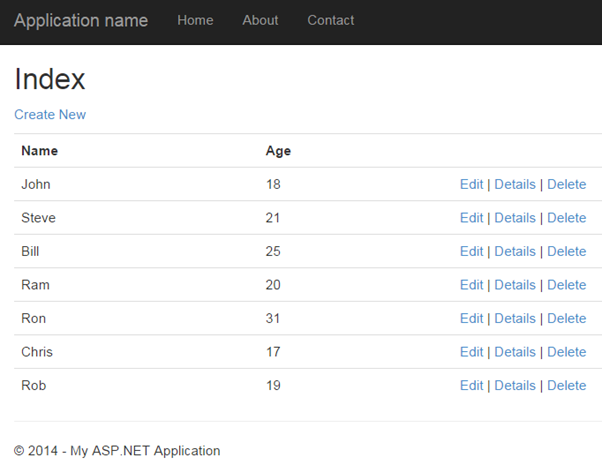
Learn razor syntax in the next section.